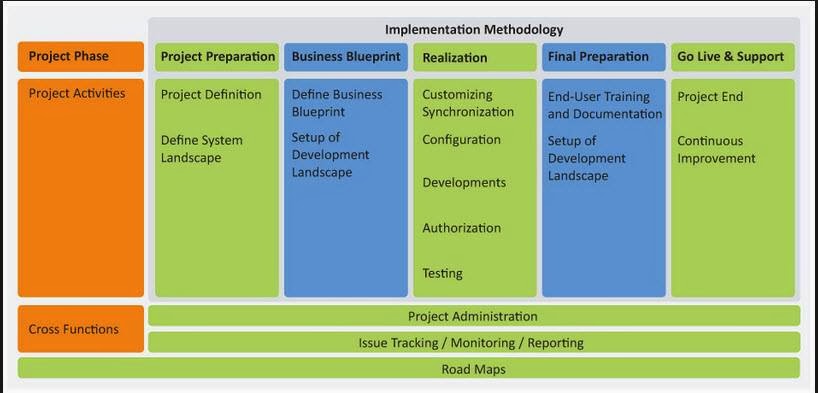
IMPLEMENTATION METHODOLOGY IN SAP
IMPLEMENTATION METHODOLOGY IN SAP
PROJECT PHASE: A stage
of a project . You can specify project phases to suit your requirements.
Examples of project phases for a pharmaceutical R&D
organization are Discovery, Pre-Clinical I, Pre-Clinical II, and Clinical
Trial.
PROJECT ACTIVITIES: A
detailed description of a task in a work package in the R/3 Procedure Model .
Project activities also serve as convenient structural units in detailed
project planning and project management.
Implementation
projects are divided into the following phases:
1. Project
Preparation.
2. Business Blueprint.
3. Realization.
4. Final Preparation.
5. Go Live &
Support.
1.PROJECT PREPARATION :
During Project
Preparation, you plan and prepare R/3 project implementation by defining your
project goals and objectives, the scope of your implementation, your
implementation strategy, the project schedule and implementation sequence. You
also set up the project team in this phase.
The main purpose of Project Preparation phase is to help
carry out the initial planning and preparation for the SAP CRM project. The
strategy that will be followed for the implementation, such as the resources
that will be involved, the landscape strategy, the sequence of implementation
and finally getting all the above mentioned approved and signed off by the
client.
A).PROJECT DEFINITION:
ACCORDING TO SAP: A summary of goals, plans, processes, tasks, timelines, and resources within a collaborative enterprise. A project has defined costs and a defined budget based on the tasks involved.
B).DEFINE SYSTEM LANDSCAPE:
ACCORDING
TO SAP: Any required systems and clients, their meaning and the
transport routes for implementation and maintenance processes.
Relevant tools in this context include Client Copy and the Change
and Transport System.
The system landscape may, for example, comprise a development
system, a test system, and a production system.
2.BUSINESS BLUEPRINT: The purpose of this phase is to understand
the requirements of the client through requirements gathering. The resulting
document is called the Business Blueprint. This also helps to achieve a common
understanding of how the company intends to run its business within the SAP CRM
system. The following would form a part of the Business Blueprint:
AS
IS – Helps understand the existing business process.
TO
BE – Based on AS IS, we look at how the business process can be mapped in SAP
and if any changes have to be carried out to the existing business process if
required.
Gap
Analysis – This analysis is carried out to identify the inputs or business
processes that cannot be mapped in SAP. Gap document is created to be analyzed
further to identify a solution to bridge the gap.
A).BUSINESS
BLUEPRINT DEFINTION: The purpose of this phase is to create the
Business Blueprint document, which details business processes and other
objectives identified during the requirements workshop. You also use the
Business Blueprint to define the Baseline scope and refine the original goals
and objectives and the project schedule.
BUSINESS
BLUEPRINT DOCUMENT: The main
deliverable of the Business Blueprint phase. The Business Blueprint document
provides written documentation of the results of the requirements-gathering
sessions. It verifies that a proper understanding of requirements has been
communicated. This document also finalizes the detailed scope of the project.
B).DEVELOPMENT
LANDSCAPE: Consists of multiple successive tracks.
Mutually independent software components are developed in each track. Software
components that are developed in successor tracks can be based on the software
components of their predecessor tracks and define dependencies.
3.REALIZATION: The purpose of
this phase is to implement business and process requirements contained in the
Business Blueprint in the SAP System to set up and configure the R/3 System,
and to draw up user documentation and training material.
Prototyping solutions and testing is done during the
realization phase. In this phase we implement all the business process
requirements based on the business blueprint. We define the test plans for
system tests, data tests, data access tests and authorizations tests. We also
establish the SAP CRM administration procedures.
A).CUSTOMIZING SYNCHRONIZATION: Tool to
synchronize settings in selected customizing objects in a source system, e.g.
SAP R/3, with customizing in target systems, e.g. SAP CRM system.
Customizing synchronization comprises a cross-component comparison
and customizing distribution.
B).CONFIGURATION: The definition
of parameters that an SAP program uses to determine, for example, display
modes, available functions and components, network communications, and
connections with other programs.
C).DEVELOPMENTS: A system in which
customer developments and customizing settings are made. The
system data can be transferred from here to the quality assurance system.
D).AUTHORIZATION : The authority to execute a
particular action in the SAP System.
Each authorization references an authorization object and defines
one or more permissible values for each authorization field contained in the
authorization object. Authorizations are combined in profiles, which are
entered in a user's master record.
E).TESTING:
During the entire life cycle of a SAP solution, it is
necessary to test the functions and performance of your solution. With the SAP
Test Workbench, SAP provides you with an environment for all test phases, which
you can use for testing in the following cases:
a)
Implementation of SAP solutions
b)
Integration of new components and
business scenarios
c)
Customer developments
d)
Function tests
e)
Integration tests with other
components
f)
Upgrades, regression tests
g)
Importing support packages.
4.FINAL
PREPARATION: It builds a framework for completing final testing,
training users, and preparing for cutover of both the data and the system to a
production environment.
In this phase, we finalize the activities to roll out the SAP
CRM system to the end-user community. The end-user training, final tuning and
approval for going live is obtained. Before the Go-live phase a Cutover
strategy is carried out which involves the migration of the Master Data and the
Transaction Data from Legacy system to SAP system.
A).END USER TRAINING: Training
a).A
person or corporation to which an Authorized Reseller licenses and distributes
the Qualified Software for internal business use,
(or)
b).A person or corporation to which an
authorized channel partner licenses and distributes the N-Tier Software for
internal business use.
END USER
DOCUMENTATION: Company-developed documentation for users, to be used in
training prior to going live, as well as referenced for policy and procedures. Business
Process Procedures can serve as the starting point for user documentation.
B).DEVELOPMENT
LANDSCAPE: Consists of multiple successive tracks.
Mutually independent software components are developed in each track. Software
components that are developed in successor tracks can be based on the software
components of their predecessor tracks and define dependencies.
5.GO LIVE
& SUPPORT: The
purpose of this phase is to move from a pre-production environment to live
production operation, to set up a Help Desk to provide long-term support for
users and optimize overall system performance and the technical environment.
You also use this phase to plan follow-up training, upgrades and ways to
continually optimize the SAP System.
The purpose of the Go-live phase is to roll out the SAP CRM
system to the end users in a live business environment. All the transactions,
data and the system is monitored in the live environment. This phase also provides
up to 2 weeks of post Go-live support, which is dependent on the agreement with
the client. Any optimization that is required, is taken care of during this
support phase. Normally, large companies have maintenance support contracts
with SAP and get support on a global scale, up to 24/7 – based on the Service
Level Agreement (SLA).
PROJECT END : End of the
project.
CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT: Operations
and Continuous Improvement, to continuously optimize the SAP system.
CROSS FUNCTION: A key functional area of mySAP Technology
that supports specific requirements such as replication and realignment of
laptops for mySAP Customer Relationship Management(CRM) and high performance
memory-based computing for mySAP Supply Chain Management(SCM).
PROJECT
ADMINISTRATION: Function in the administrator role for
managing projects. Project administration enables you to perform activities
such as deleting projects.
ISSUE
TRACKING: Tracking a problem or
project situation that affects project goals. An issue may result in changes to
scope, budget, timeline, or resources. Issues are managed using Issues
Management(Tool to document and manage unresolved problems in an SAP implementation
project.).Upon review of an issue, a remediation plan may be implemented to
resolve or deal with the issue identified.
MONITORING
: The process of collecting
and displaying data and metrics from the SAP system and its components (for
example, dialog instance, central instance, database instance), the
virtualization layer, and the physical system.
REPORTING: The classical application area of
executable programs. The program flow follows the EVA principle: A selection
screen is displayed, data is imported (often using a logical database) and the
processed data is displayed in a formatted list. The selection, summarization
and presentation of data from application systems.
ROAD MAP: A methodological
framework for implementing, upgrading or continually improving your SAP
software .The Roadmap structures implementation projects into five phases and
provides detailed project plans in Microsoft Project format to support your
planning process. Each level of the ASAP Roadmap structure includes
documentation that contains recommendations for your implementation project,
information on tools, links to accelerators, and information from SAP Net and the
World Wide Web.
REFERENCES :
For Project Preparation :
For Business Blue Print :
For Realization:
For Final Preparation:
For Go live & Support:
For Project Administration:
For Complete Implementation Methodology:

Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts let me know